

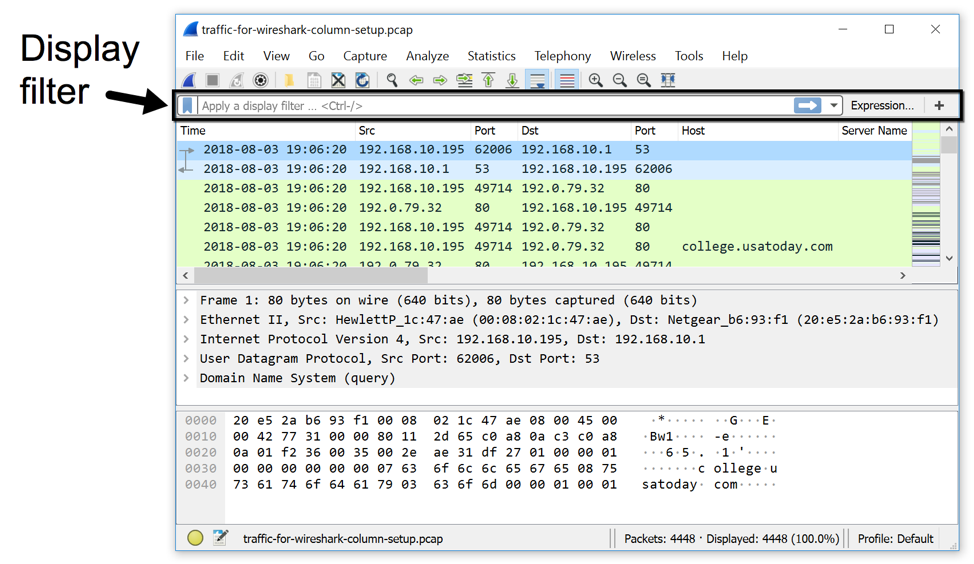
Now you can type in a Wireshark display filter expression. Issue a sleep in the pane for /dev/pts/10 so that no other process reads from the terminal while it is dedicated to termshark. $ termshark -r file.pcap -T psml -n | lessīy default, termshark will launch an ncurses-like application in your terminal window, but if your standard output is not a tty, termshark will simply defer to tshark and pass its options through: You can provide tshark-specific flags and they will be passed through to tshark (-n, -d, -T, etc). If -pass-thru is true (or auto, and stdout is not a tty), tshark will be executed with the supplied command-line flags.
Arguments: FilterOrPcap: Filter (capture for iface, display for pcap), or pcap to read. (default: auto) -log-tty Log to the terminal. pass-thru= Run tshark instead (auto => if stdout is not a tty). C, -profile= Start with this configuration profile. t= Set the format of the packet timestamp printed in summary lines. D Print a list of the interfaces on which termshark can capture. Usage: termshark Application Options: -i= Interface(s) to read. Analyze network traffic interactively from your terminal. $ termshark -h termshark v2.4.0 A wireshark-inspired terminal user interface for tshark.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
